Smart LED lighting will record the highest growth of IoT consumer applications,
from 6 million units in 2015 to 570 million units by 2020.
~Source: Gartner, 2015
LED Technology
Evolution of light by human being dates back to incandescent light. Today, LED technology has proved to be the most efficient system. A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor (electrical) device, that restricts current flow in one direction. Semiconductor diodes are comprised of two regions, one is p region (positive charges) and other is n region (negative charges). When voltage is applied, the electrons move across the n region into the p region. During the process of an electron moving through the p-n junction, it releases energy. The dispersion of this energy produces visible light.
LED Lighting Colours
LED Lighting can come in many different colours, the most common of these in household usage lights are Warm White, Neutral White and Cool White. Lighting colours Warm White with a Kelvin rating of 2700K-3300K, Neutral White with a Kelvin ranging from 5500K-6000K, Cool White with a Kelvin rating of 6000K-6500K.

Colour Rendered Index (CRI)
CRI is a measurement technique, to define how well a given object displays the true colours of an object. The general colour rendering index rates colour rendering out of 100(100 being the sunlight). The higher the index, the better the colour rendering and different light sources have different colour rendering characteristics.
Benefits of LED Lights
High Efficacy
Efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Latest lab data showed efficacy more than 250 lm/W. However, in real lighting fixture we must consider several factors such as control gear performance, luminous flux depreciation with increasing junction temperature, optical losses etc., which reduce the overall system efficacy.
“Efficacy increase over the time for various light sources.”
Environmental Impact
Using LEDs reduce environmental impact in several areas. Longer lamp life means that fewer resources are required for maintenance. They also use no mercury and less phosphorus than fluorescent alternatives. These facts combined with high efficiency make LEDs a smart choice while reducing the footprint on the nature.
Controllability
LEDs can be integrated into the electronic control system which allows for control of color balance and intensity, independent of each other while maintaining color rendering accuracy. This is impossible with traditional light sources. For general illumination, LEDs can dim from 0.1 % to 100 %.
Durability
LEDs are highly rugged. They incorporated no filament or fragile glass bulb that can be damaged due to mechanical vibrations and shocks. LED light fixtures are especially appropriate in applications with strong probability of lamp breakage such as bridges, industrial areas, or stadiums.
Low-temperature operation
Low temperatures present a challenge for fluorescent lamps. At low temperatures, higher voltage is required to start fluorescent lamp, and luminous flux is decreased. In contrast, LED performance is inherently increased at low operating temperatures. This feature predestines LEDs for grocery stores, cold storage facilities, and outdoor application.
No UV emissions/ Health aspects
LEDs emit light with negligible ultraviolet (UV) and very little infrared radiation. Small amount of radiated heat by LEDs makes them appropriate for goods which are sensitive to heat. The lack of UV radiation (with appropriate design of optical part) makes them an attractive also for illumination of delicate objects such as artworks as well as materials subject to UV degradation.
"When LED light is used in delicatessen displays and in places with fresh food, it has been proven to breed significantly less bacteria than their halogen or fluorescent counterparts."
~lightology
LED vs Other Sources of Light
Incandescent or fluorescent bulb emits light and heat in all directions. For direct lighting applications LED lighting uses both light and energy more efficiently. For example, an incandescent or compact fluorescent (CFL) bulb inside of a recessed can will waste about half of the light that it produces, while a recessed down light with LEDs only produces light where it's needed.
| Lamp Type | Incandescent buld | Halogen lamp | Metal halide lamp | Mercury vapor lamp | LED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficacy (lm/W) | 6-16 | 16-30 | 75-125 | 40-75 | 80-160 |
| Input power: (W) | 20-60 | 55-100 | 20-24000 | 50-500 | 0.2-100 |
| Hazardous chemical content: | no | Halogens | Argon, Mercury | Argon, Mercury | no |
| Electronics ballast: | no | In general no | needed to control the current | needed | needed |
| CRI: | 100 | 100 | 70-95 | 40-60 | 65-97 |
| Application: | Indoor, outdoor | Indoor applications like shops, residential | Floodlight, outdoor, shops | Outdoor applications, streetlights, facade | Indoor, Outdoor |
| Additional Information: | high IR radiation | high IR radiation | High UV radiation | High light pollution | little UV and IR radiation |
| Lifetime : (hours) | 1000 | 1000-3000 | 6000-20000 | 4000 | 50000 |
| CCT | 2700 | 2700-3500 | 3800-7000 | 3200-4200 | 2700-8000 |
| Dimmable | yes 0-100% | yes 0-100% | yes 50-100% | no | yes 0.1-100% |
Lumens in Lighting
Way back in 1960s, a bulb was measured by its ‘candle power’. One would ask for a 40-candle bulb and be sure to get light equal to 40 candles. Over the years, the smart businessman changed it quietly to 40 Watts. The common man never realised the smooth transition to this word “watt”, and assumed 40 watts was equal to 40 candles. No. It is not. 40 watts consumes 40 watts power, but doesn’t deliver 40 candles of light.
Therefore, it is imperative for us to know the worth of light for the watts burned by bulb. The measure of light is called Lumens.
Lumens measure how much light you are getting from a bulb. More lumens mean it's a brighter light; fewer lumens means it's a dimmer light.
- Lumens are to light
- Pounds are to bananas
- Gallons are to milk
Lumens let you buy the amount of light you want. So, when buying your new bulbs, think lumens, not watts.
The brightness, or lumen levels, of the lights in your home may vary widely, so here's a rule of thumb:
To replace a 100-watt incandescent bulb, look for a bulb that gives you about 1600 lumens. If you want something dimmer, go for less lumens; if you prefer brighter light, look for more lumens.
Replace a 75W bulb with an LED bulb that gives you about 1100 lumens
Replace a 60W bulb with an LED bulb that gives you about 800 lumens
Replace a 40W bulb with an LED bulb that gives you about 450 lumens
“Think Lumens, Not Watts”
Application Areas of LED Lights
Explore our Innovative LED Lighting Solutions
Explore SolutionsFrequently Asked Questions
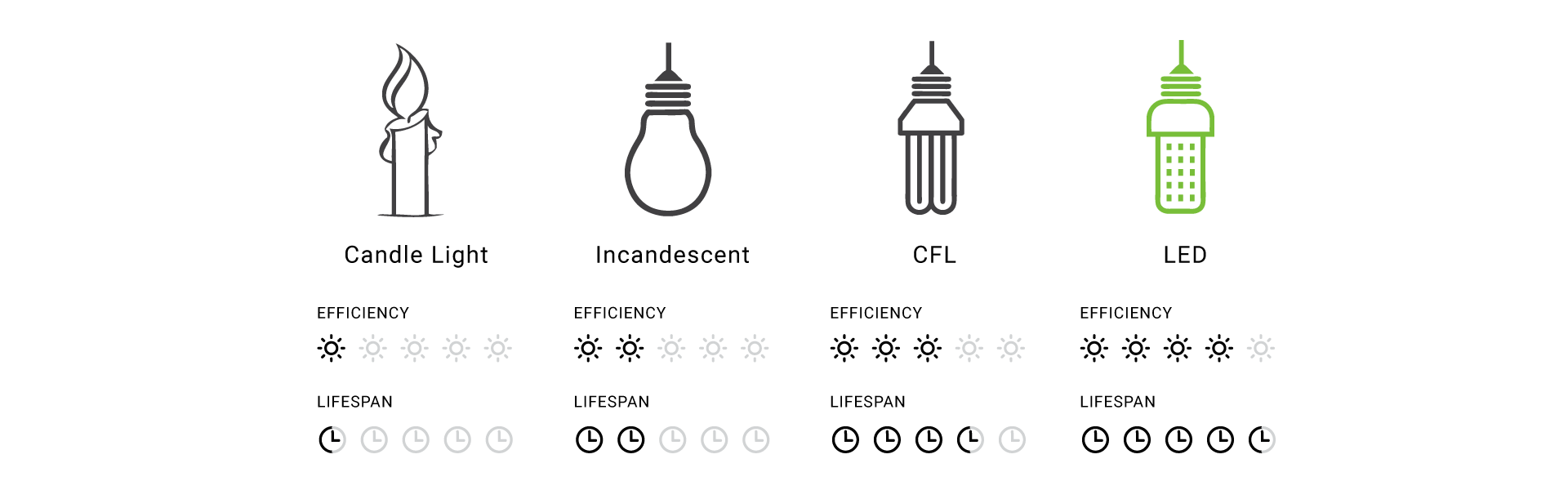
- A typical incandescent lamp lasts about 1,000 hours.
- A comparable CFL lasts 8,000 to 10,000 hours.
- An LED Light Lasts for 50,000 hours or even longer.
Normalized to Incandescent lamp life. Lumen depreciation of different light sources will be as follows.
- Incandescent-10-15 %
- CFL- 2%
- LED-0.6%
The effect of temperature on LED lights is
Operating temperature
Operating temperature of the light is the range of temperature over which the device operates without any malfunction and delivers its rated output.
Effect of temperature raise above ambient when in use
Excess heat directly affects short term and long-term LED performance. The short term (reversible) effects are
- Colour shift
- Reduced Light output
- Long term (irreversible permanent) effects
- Accelerated lumen depreciation and shortened useful life.
- Efficacy. Minimum 100L/watt
- >CRI
- Low Operating Temperature
- Electric Power
- Warranty
- Durability
- Glare free
- At least 5 year warranty
Key differences include the following:
Direction: LEDs Lights emit almost all their light output in the direction, rather than dispersing it in all directions. Whereas CFL Lights emit light in all directions.
Colour Rendering Index: Colour Rendering Index is an index rating commonly used to represent how well a light source reproduces the actual colour of object that it illuminates.
LED Lights produce nearly 70-80% of heat for unit input power. An increase in the junction temperature of the LED has an adverse effect on the light output. The rise in junction temperature results in decrease of light output from the LED package. This results in:
- Decrease in light output
- Colour Shift
- Lumen Depreciation